스포트라이트
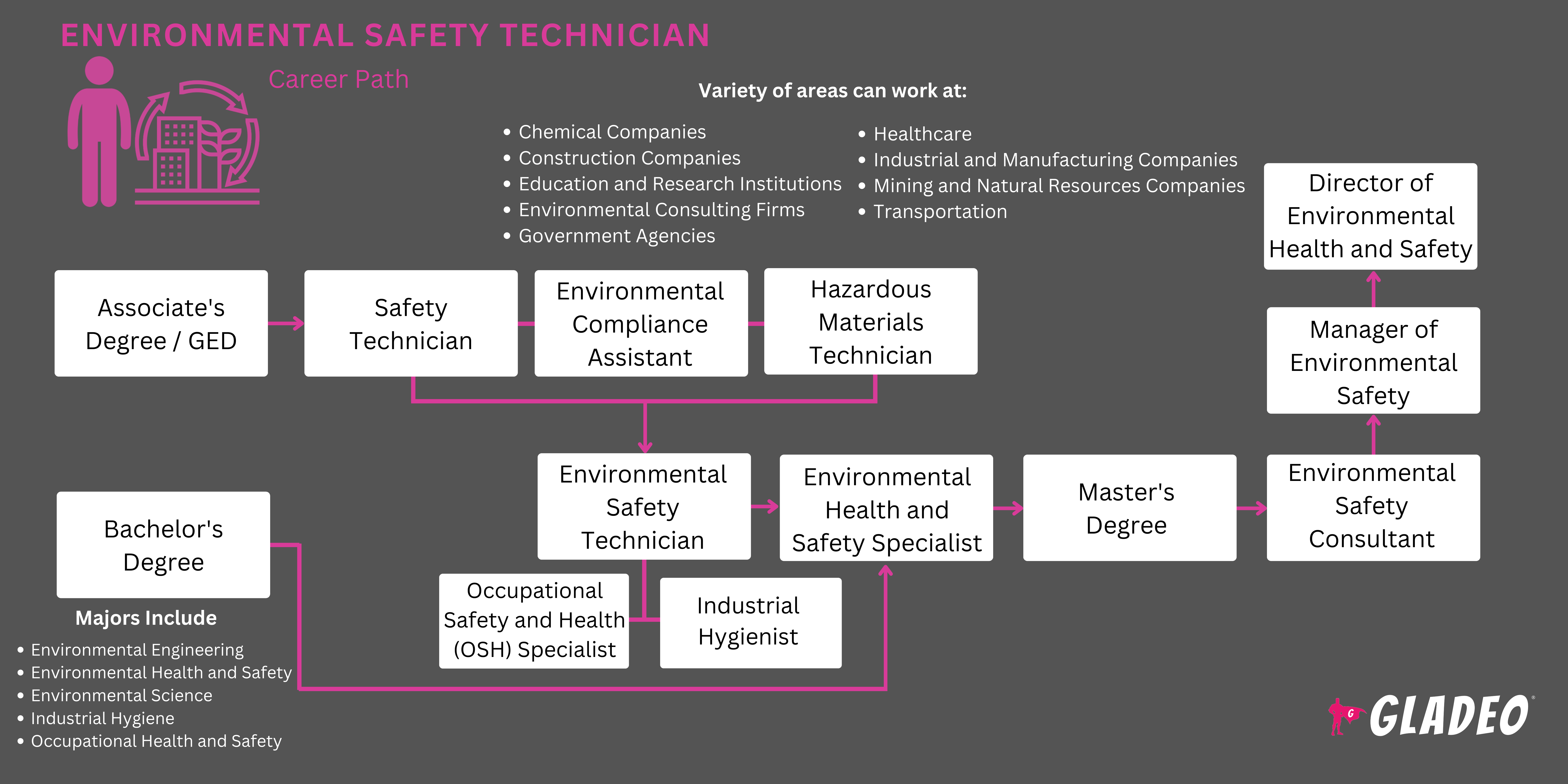
Environmental Health and Safety Technician, Environmental Compliance Technician, Hazardous Materials Technician, Occupational Health and Safety Technician, Industrial Hygiene Technician, Environmental Monitoring Technician, Safety Coordinator
Some industries, like energy production, transportation, manufacturing, and agriculture, have a larger impact on the environment than others. At the same time, these industries are also among the most hazardous to work in.
Since the operations of these types of industries have the potential to harm workers and the environment, they have experts assigned to help ensure compliance with safety and environmental regulations.
Known as Environmental Safety Technicians, their job includes monitoring conditions, identifying hazards, assessing risks, and proposing solutions to mitigate risk. They also conduct inspections to make sure employers and employees follow the right procedures so that workers, communities, and ecosystems are as safe as possible.
- Implement and monitor environmental safety programs
- Contribute to pollution reduction and environmental protection
- Ensure compliance with workplace safety and health regulations and policies
- Play a key role in emergency preparedness and response
근무 일정
Environmental Safety Technicians typically work full-time. Overtime may be required for emergency response situations or to meet project deadlines. Some travel may be necessary for site evaluations.
일반적인 의무
- Monitor workplace environmental conditions; check for adherence to regulations
- Apply codes, regulations, laws, and policies related to worker health and safety
- Conduct inspections and audits to identify potential safety hazards and environmental risks. Ensure safe levels of air and water quality
- Check emission control devices for proper functioning
- Collect and analyze samples of soil, water, and gas for contaminants and pollutants, following Environmental Protection Agency guidelines
- Analyze and interpret environmental data using modeling, simulation tools, and Geographic Information Systems
- Assist in developing and implementing safety programs and emergency response plans to safeguard workers against hazardous practices and materials
- Communicate safety-related information to employees, managers, and contractors
- Provide workplace safety training; document training records, as needed
- Ensure proper use of safety equipment and personal protective equipment
- Research Safety Data Sheets, perform Toxic Substances Control Act assessments, authorize chemical use, and administer chemical tracking
- Follow guidelines in the Resource Conservation and Recovery Act
- Develop data-driven action/mitigation plans, including testing and treating Acid Mine Drainage water
- Review Stormwater Pollution Prevention Plans to ensure compliance with Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) standards
- Provide support in hazardous waste management labeling, storage, transport, and disposal
- Assist in applying for environmental and health safety permits
- Analyze incident data for trends in mishaps, injuries, and hazards
추가 책임
- 테스트 기기 보정
- Cooperate with external inspections
- Implement Spill Prevention, Control, and Countermeasures, as applicable
- Conduct monitoring and reporting to government agencies as required
- Maintain records related to waste characterization
- 사건 및 사고에 대한 조사 지원, 근본 원인 파악 및 예방 조치 권장
- Prepare reports based on assessments, audits, inspections, and investigations
- 신입 기술자 교육 및 감독
- Participate in sustainability initiatives and meetings
- Research trends, best practices, and regulatory changes
소프트 스킬
- 분석
- 세부 사항에주의
- 합작
- 비판적 사고
- 연역적이고 귀납적인 추론
- 디테일 지향
- 독립의
- 무결성
- 모니터링
- 목표
- 조직
- 통찰력
- 문제 해결
- 독
- 안전 지향
- 힘과 체력
- 강력한 의사 소통 기술
기술 능력
- Emergency response planning
- Environmental areas (e.g., air quality, water resources)
- 환경 모니터링, 샘플링, 데이터 수집 및 분석 도구와 기술
- 환경 규제 및 규정 준수 조치
- 환경 보고 도구
- Environmental science and ecology
- 지리 정보 시스템(GIS)
- Hazardous waste and materials regulations and handling procedures
- 프로젝트 관리
- 보고서 작성 및 프레젠테이션
- 안전 및 보건 평가 기법
- Statistical and data modeling tools
- Chemical companies
- Construction and infrastructure companies
- Corporate environmental departments
- 환경 컨설팅 회사
- 정부 규제 기관(연방, 주, 지방)
- 의료 시설
- Industrial and manufacturing plants
- Mining and natural resource companies
- Public and private educational institutions
- Research organizations
- Utilities (water, gas, and electric)
- Waste management and recycling companies
Environmental Safety Technicians may work in various conditions, including industrial settings or outdoors facing environmental factors. The job may require being around hazardous materials, which demands strict adherence to safety protocols.
Workers sometimes face industry resistance or public concerns, requiring them to have strong communication skills. As advocates for workplace safety and environmental stewardship, they play a crucial role in promoting and implementing effective health and safety practices and policies. At the same time, they must engage in continuous learning to stay updated on changing regulations and safety practices.
The public is putting pressure on governmental agencies to do more for the environment and to have more oversight on what organizations are doing. This push for more sustainability and accountability is resulting in new laws and updated policies and regulations at national, state, and local levels.
Environmental Safety Technicians help to explain these changes and monitor organizational compliance with them. Technology like remote sensing and advanced analytical tools is enabling them to conduct more precise monitoring and better data collection.
The incorporation of AI, wearable smart devices, robotics, and electronic reporting systems is also being used to enhance safety—but these advancements require workers to keep up with the evolving technologies.
Students who choose to become Environmental Safety Technicians often have an interest in the natural world and environmental conservation. They may have been involved in science clubs, outdoor activities, and community initiatives focused on sustainability from a young age. Their academic interests probably included subjects like biology, chemistry, and environmental studies.
- Environmental Safety Technicians typically require an associate degree, technical certification, or in some cases a bachelor’s degree
- Note, some entry-level positions may only require relevant work experience versus academic credentials
- Common degrees include:
- Associate degree in Environmental Science
- Associate degree in Occupational Health and Safety
- Bachelor’s in Environmental Engineering
- Bachelor’s in Environmental Health and Safety
- Bachelor’s in Environmental Science
- Bachelor’s in Industrial Hygiene
- Bachelor’s in Occupational Health and Safety
- 관련 교과 과정에는 다음이 포함될 수 있습니다:
- 공기 품질 관리
- Climate Change and Global Warming
- Conservation Biology
- 생태학
- Environmental Health and Toxicology
- 환경 영향 평가
- Environmental Law and Legislation
- 지리 정보 시스템(GIS)
- Hazardous Materials Handling
- Industrial Safety
- Natural Resource Management
- Occupational Health and Safety
- Renewable Energy Sources
- Soil Science
- Waste Management
- Hands-on experience through internships, research assistant roles, or entry-level environmental health and safety jobs can be beneficial
- In addition, expect a few months of on-the-job training
- Optional industry certifications include:
- Hazardous Waste Operations and Emergency Response certification
- 공인 위험물 관리자
- Occupational Hygiene and Safety Technician
- 공인 환경 전문가
- 근로자가 작업 현장으로 이동하려면 유효한 운전면허증이 필요할 수 있습니다.
- Environmental Safety Technicians can receive training at community colleges, universities, or even at technical or vocational schools
that offers programs or certifications in environmental safety - Look for accredited schools offering programs in environmental science, environmental health and safety, occupational health and safety, industrial hygiene, or environmental engineering
- 캠퍼스, 온라인 또는 하이브리드 프로그램에 등록할지 여부를 결정할 때 일정과 유연성에 대해 생각해보십시오.
- Seek programs with fieldwork and internships opportunities
- 수업료, 할인 및 지역 장학금 기회 비용을 고려하십시오 (연방 지원 이외에)
- 외부 파트너와 협력하여 학습 경험을 강화할 수 있는 프로그램을 찾아보세요.
- 졸업률 및 졸업 후 취업 통계 검토하기
- Ask a seasoned Environmental Safety Technician to do an informational interview with you, or see if you can shadow them at work for a day
- Watch videos and read online articles related to the career field to familiarize yourself with current environmental health and safety trends. Popular blogs include:
- 고용 포털에 게시된 직무 설명을 확인하여 가장 최신의 직무 자격 요건과 관심 있는 전문 분야를 확인하세요.
- In high school, load up on biology, ecology, chemistry, environmental science, math (especially algebra and geometry), physics, health science, geography, English, writing, computer science, government, and shop classes
- Engage in extracurricular activities to gain teamwork, leadership, and project management experience
- Participate in relevant online forums like the National Safety Council’s Global Health, Safety & Environment Forum
- 이력서 및 대학 지원서를 위해 모든 업무와 학업 성취도를 추적하세요.
- Upload your resume on job portals like Indeed, SimplyHired, Monster, USAJobs, ZipRecruiter, Velvet Jobs, and Glassdoor
- 새 채용 공고가 올라올 때 놓치지 않도록 알림을 신청하세요.
- 구인 광고를 검토하고 이력서에 기재할 키워드를 찾아보세요:
- Accident Prevention
- 긴급 대응
- Environmental Compliance
- Environmental Management Systems
- EPA Regulations
- Hazardous Materials Management
- Health and Safety Programs
- Incident Investigation
- 산업 위생
- OSHA Standards
- Policy Development
- Risk Assessment
- Safety Audits
- Safety Regulations
- Safety Training
- Workplace Safety
- Review Environmental Safety Technician resume templates and sample interview questions
- 학교에 채용 담당자와 연결해 달라고 요청하세요. 환경 안전 관련 기관에서 인턴으로 일할 기회를 활용하세요.
- 학교의 커리어 센터에 연락하여 이력서 도움을 받고, 모의 면접을 하고, 예정된 취업 박람회에 대해 알아보세요.
- 다음과 같은 잠재적인 대형 고용주에 대해 조사하세요:
- 질병 통제 예방 센터
- Department of Defense
- 에너지부
- 환경 보호국
- 연방재난관리청
- National Aeronautics and Space Administration
- 국립 보건원
- 산업안전보건청
- 미국 농무부
- United States Geological Survey
- 면접 시 업계 동향에 대한 예리한 인식을 보여주세요.
- 면접을 위한 전문성 있는 복장
- 이전 교수 및 지도교수에게 추천서를 작성해 달라고 요청하거나 추천인으로 등록하는 데 (사전에) 동의를 요청하세요.
- Speak with your supervisor about advancement. Get advice and talk through options
- Show your willingness to learn, follow procedures, and assume increased responsibilities
- Set the bar high and ensure compliance with regulations to help protect workers, equipment, facilities, work sites, and surrounding areas
- 전문성 개발 및 평생 교육 과정 수강에 적극적으로 참여하세요.
- Knock out additional certifications when qualified to do so, like the Board of Certified Safety Professionals - Associate Safety Professional
- If beneficial, consider doing a higher-level college degree
- Try to gain diverse experience across different workplace environments. After working in different areas, consider specializing in a particular area such as:
- Accident Investigation
- 공기 품질 관리
- Biological Safety
- Chemical Safety
- Construction Safety
- Emergency Response Planning
- Environmental Compliance
- Ergonomics
- Fire Safety and Prevention
- 유해 폐기물 관리
- 산업 위생
- Noise Control and Hearing Conservation
- Occupational Health
- Radiation Safety
- Regulatory Compliance and Auditing
- Risk Assessment and Management
- Safety Engineering
- Sustainability and Environmental Protection
- Water Quality Management
- Workplace Safety Training
- Be active in professional organizations such as the American Industrial Hygiene Association (see our list of Recommended Resources for more information)
- Keep current on changes related to employer policies and local, state, or federal regulations
웹사이트
- 이사회 인증 환경 전문가 아카데미
- 엔지니어링 및 기술 인증위원회
- 공기 및 폐기물 관리 협회
- 미국 환경 공학 및 과학자 아카데미
- 미국 화학 학회
- 정부 산업 위생사의 미국 회의
- 미국 산업 위생 협회
- 미국 모기 통제 협회
- 미국 국립 표준 협회
- 미국 공중 보건 협회
- 미국 미생물학 학회
- 미국 안전 전문가 협회
- ASTM 인터내셔널
- 글로벌 EHS 자격 증명 위원회
- 전문 인체 공학의 인증위원회
- 공인 안전 전문가 위원회
- 질병 통제 예방 센터
- 산업 공학 협의회
- Department of Defense
- 에너지부
- 에너지 스타
- 환경 보호국
- 연방재난관리청
- Health Physics Society
- 유해 물질 관리 연구소
- 공학 및 기술 연구소
- International Society for Sustainability Professionals
- 국제 자동화 협회
- International Society of Exposure Analysis
- 에너지 및 환경 디자인 리더십(LEED)
- National Aeronautics and Space Administration
- 국립 환경 관리 협회
- 전국 환경 전문가 협회
- National Association of Safety Professionals
- 공중 보건 심사관의 국가 위원회
- 엔지니어링 및 측량을위한 전국 심사관 협의회
- 국가 환경 건강 협회
- 전국 소방 협회
- 국립 엔지니어링 기술 인증 연구소
- 국립 산업 안전 보건 연구소
- 국립 보건원
- 국립 레크리에이션 및 공원 협회
- 환경 전문가의 국가 등록
- 국가 안전 위원회
- NSF International
- 산업안전보건청
- 규제 업무 전문가 협회
- Society for Mining, Metallurgy and Exploration
- 미국 그린 빌딩 협의회
- 미국 농무부
- United States Geological Survey
- 세계 안전 기구
책
- Safety Risk Management: Preventing Injuries, Illnesses, and Environmental Damage, by Fred Fanning
- Safety WALK Safety TALK: How small changes in what you THINK, SAY, and DO shape your safety culture, by David Allan Galloway
- The Beginner’s Guide to the Environmental, Health and Safety Profession, by Chance Roberts
Environmental Safety Technicians play a crucial role in protecting our workers, communities, and natural environment. But this career isn’t the right fit, consider related fields that might interest you, such as:
- 브라운필드 재개발 전문가
- 자연 보호 과학자
- 건설 및 건축 검사관
- 환경 규정 준수 검사관
- 환경 공학 기술자
- 환경 과학자
- 화재 검사관
- Geological Technicians
- 유해 폐기물 기술자
- 보건 및 안전 엔지니어
- 수문학자
- 산업 위생사
- 재료 과학자
- 미생물 학자
- 광업 및 지질 공학자
- 산업 보건 및 안전 전문가
- Public Health Officer
- 보안 관리자
- 수처리/폐수 엔지니어
- 수자원 전문가
- 야생 생물 학자
뉴스 피드
주요 채용 정보

온라인 과정 및 도구








